In the quest for a healthier lifestyle, diet plays a pivotal role. The Mediterranean Diet and the Western Diet are two of the most talked-about dietary patterns today. Each has its own unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. In this article, we’ll delve into a detailed comparison of these two diets, helping you make an informed choice for your health journey.
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet
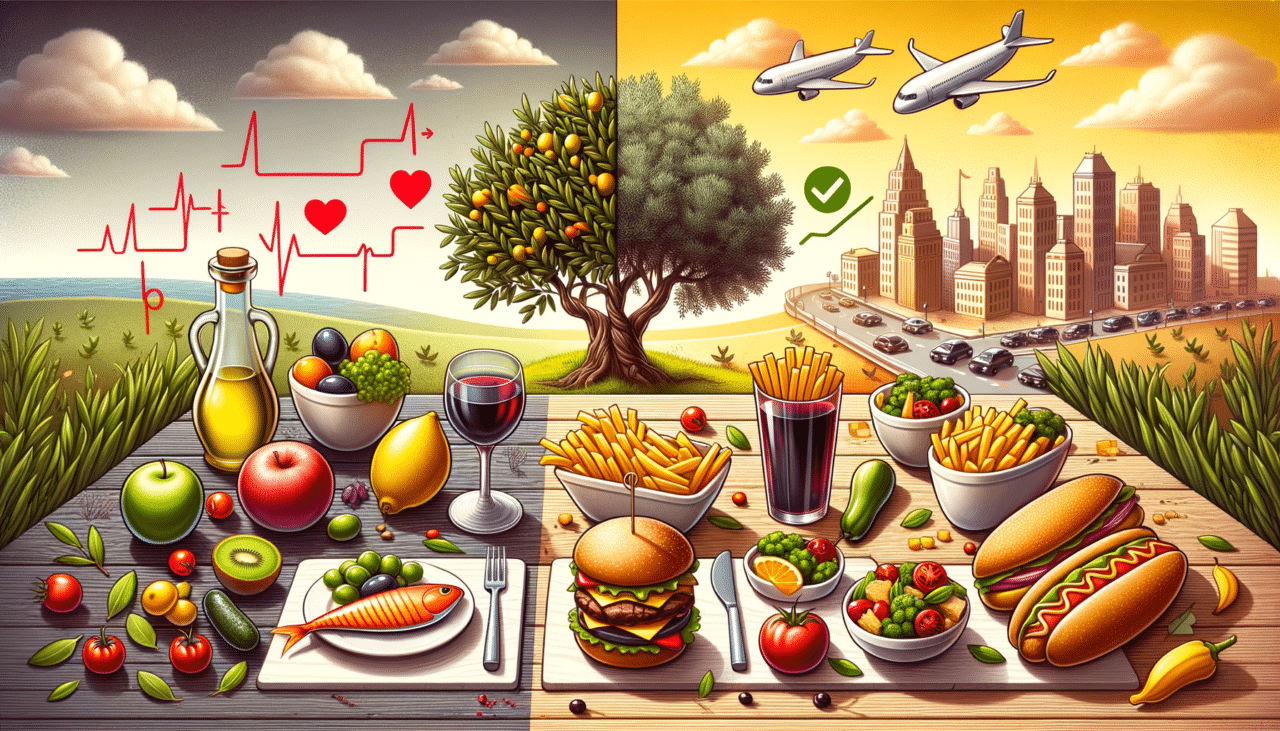
The Mediterranean Diet is inspired by the traditional eating habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. This diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods, and is renowned for its health benefits, particularly in promoting heart health.
Key Characteristics of the Mediterranean Diet:
- High in Healthy Fats: Predominantly utilizes olive oil as the primary source of fat, which is rich in monounsaturated fats.
- Plant-Based Foods: A high intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Whole Grains: Focus on whole grains like barley, oats, and whole wheat.
- Moderate Protein: Includes moderate consumption of fish and poultry, with limited red meat.
- Dairy Products: Primarily low-fat or fat-free options, like yogurt and cheese.
- Herbs and Spices: Used liberally to flavor food instead of salt.
- Social and Physical Aspects: Encourages meals with family and friends, along with regular physical activity.
Health Benefits:
- Heart Health: Reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Weight Management: Supports weight loss and maintenance.
- Reduced Inflammation: Thanks to the high intake of antioxidants from fruits and vegetables.
- Improved Mental Health: Associated with a lower risk of depression.
Understanding the Western Diet
The Western Diet, also known as the Standard American Diet (SAD), is characterized by its high intake of processed foods, red meat, and sugar. This diet is often linked to increased health risks and is prevalent in many developed countries.
Key Characteristics of the Western Diet:
- High in Saturated Fats: Predominantly includes butter, red meat, and processed meats.
- Processed Foods: High consumption of packaged snacks, fast food, and ready-to-eat meals.
- Refined Grains: Includes white bread, pastries, and other refined carbohydrate sources.
- High Sugar Intake: Sugary drinks, candies, and desserts are common.
- Low in Fruits and Vegetables: Generally lacks adequate servings of fresh produce.
- Convenience Over Nutrition: Focuses on quick and easy meal options.
Health Risks:
- Heart Disease: Increased risk due to high saturated fat and cholesterol intake.
- Obesity: Linked to high-calorie, low-nutrient foods.
- Type 2 Diabetes: High sugar and processed foods contribute to insulin resistance.
- Poor Gut Health: Lack of fiber from fruits and vegetables affects digestion.
Comparative Table: Mediterranean Diet vs. Western Diet
| Feature | Mediterranean Diet | Western Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Fats | Olive oil, nuts, seeds | Butter, margarine, processed oils |
| Main Protein Sources | Fish, poultry, legumes | Red meat, processed meats |
| Carbohydrates | Whole grains like barley and oats | Refined grains like white bread and pasta |
| Fruits and Vegetables | High intake, variety-based | Low intake, often minimal variety |
| Dairy | Low-fat options, primarily yogurt and cheese | High-fat options, including cream and butter |
| Sugar Consumption | Low, natural sources like fruit | High, from sugary drinks and snacks |
| Meal Preparation | Homemade, emphasis on fresh ingredients | Often pre-packaged or fast food |
| Health Impact | Reduces risk of cardiovascular diseases | Increases risk of obesity and diabetes |
Conclusion
Choosing between the Mediterranean Diet and the Western Diet depends on your health goals and lifestyle preferences. While the Mediterranean Diet is associated with numerous health benefits, the Western Diet is linked to various health risks. Making small changes towards a more Mediterranean-style eating pattern can lead to significant health improvements. Incorporating more whole foods, healthy fats, and plant-based meals can not only enhance your well-being but also provide a more enjoyable eating experience.
For those seeking a healthier lifestyle, embracing the principles of the Mediterranean Diet could be a beneficial step forward. However, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals or nutritionists to tailor dietary choices that best suit your individual health needs.
By understanding the core differences between these two diets, you can make informed decisions that align with your health objectives and culinary preferences.
Comments (0)
There are no comments here yet, you can be the first!